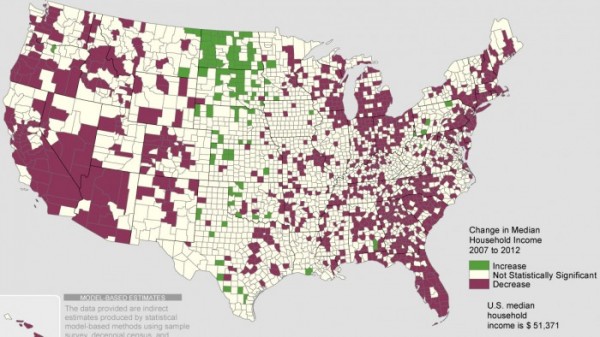
Month: December 2013
Where in the United States is median income growing?
That is from 2007 to 2012, the link is here.
Philip Tetlock’s Good Judgment Project
Philip emails me:
Your recent book was very persuasive–and I see an interesting connection between your thesis and the “super-forecasters” we have been trying to select and then cultivate in the IARPA geopolitical forecasting tournament.
One niche we humans can carve out for ourselves is, under certain fleeting conditions, out-smarting algorithms (one of the extreme challenges we have been giving our supers is out-predicting various wisdom-of-crowd indicators).You have brought us many forecasters over the years (including some “supers”) so I thought your readers might find the attached article on the research program in The Economist of interest.Our recruitment address is: www.goodjudgmentproject.com
The website writes:
The Good Judgment Project is a four-year research study organized as part of a government-sponsored forecasting tournament. Thousands of people around the world predict global events. Their collective forecasts are surprisingly accurate.
You can sign up and do it. Here is a related article from The Economist. Here is a good Monkey Cage summary of what they are doing.
Sumner on Krugman on the UK
Krugman also ignores the fact that his own graph shows fiscal policy in Britain getting more contractionary in 2013, and yet growth picked up sharply!
Read the whole thing. I also would note that the demand-side secular stagnation meme also seems to be gone or at least shelved in the cupboard, as today Krugman wrote: “Economies do tend to grow unless they keep being hit by adverse shocks.” The reallocation of labor from previous cuts in government spending is now seen unambiguously a good thing, whereas the previous argument was that in a liquidity trap such positive supply shocks could very well push economies into an even worse position. Most of all, British price inflation has continued at a robust rate and that is because of British monetary policy, again no sign of very low short rates being a “liquidity trap” in this regard. The UK labor market experience also seems to support Bryan Caplan’s repeated claims that real wage cuts really can put people back to work.
And here is a remark on timing:
I find it astonishing that Krugman and Wren-Lewis, having done post after post in 2012 describing how the UK does have real fiscal austerity in 2012, are suddenly happy to now argue that a relaxation of fiscal austerity in 2012 is the “reason” for GDP recovery in… erm, 2013.
Don’t let the emotionally laden talk of “Three Stooges” or “deeply stupid,” or continuing problems in the UK economy, distract your attention from the fact that this one really has not gone in the directions which the Old Keynesians had been predicting.
Assorted links
The Israel boycott is endorsed by the American Studies Association and Corey Robin
By a 2-1 margin, “An association of American professors with almost 5,000 members has voted to endorse an academic boycott of Israeli colleges and universities…” My earlier criticism of the boycott was here. A good Michael Kazin critique is here. Corey Robin defends the proposed boycott here. Robin’s argument is that change has to start somewhere, and we cannot boycott everything, so we might as well start with some boycotts that could work, even if that means singling out some targets unfairly.
I would start by applying a different standard. I would focus on the demands of the boycotters, and ask what is the chance that meeting those demands would work out well. The demands of the boycotters, in this case, include having Israel grant the “right of return” to Palestinians to the current state of Israel.
Now I understand the justice-based case for such a right, but what about the practicalities of such a change? The most striking feature of Robin’s boycott defense is that he doesn’t bother to argue this point.
In my untutored view, the chances that granting such rights would lead to outright civil war is at least p = 0.1, possibly much more, and the chances that such a change leads to a better outcome, in the Benthamite sense, are below p = 0.5. I readily grant these estimates may be wrong, but I don’t think they are absurdly wrong or implausible and in fact they represent a deliberate attempt on my part to eschew extreme predictions. An educated person or even a specialist might arrive at similar estimates or even more pessimistic ones. I would be curious to read Robin’s assessment.
By the way, you might think that the potential for bad outcomes is “the fault of the Israelis,” but that bears on the justice question, not on the Benthamite question. Don’t use “emotional allocation of the blame” to distract your attention from the positive questions at hand.
Why don’t we look at the world of science, where academic collaboration is actually um…useful?:
In science, however, the boycott movement has so far made comparatively few inroads.
“For us, it’s meaningless,” said Yair Rotstein, the executive director of the United States-Israel Binational Science Foundation (BSF), which was established in 1972 with an endowment funded by both countries. The boycott, he said, is something blown up in the media: for all practical purposes, “there really is no boycott.” Rotstein said that of about 7,000 requests to prospective external reviewers it sends each year, the foundation gets just one response on average from a scientist declining for political reasons.
Meanwhile, the BSF grants about $16 million in awards each year to American and Israeli scientists working on joint projects, having funded over the years, according to Rotstein, 42 Nobel Laureates. And since 2012, the BSF has partnered with the National Science Foundation to support collaborative research in biology, chemistry, computational neuroscience and computer science (The BSF gets an additional $3 million a year from the Israeli government to support these joint BSF-NSF projects.)
I still say this is not a boycott worth supporting. If we are going to do boycotts, and if we need to do boycotts, let’s do boycotts whose terms have a clearly positive Benthamite value with a minimum of extreme downside risk. There are plenty of those, and remember, we’ve been told that we need to be selective.
We’re back again to this whole thing being a lot of posturing. Note that the Palestinian government does not itself support boycotts of Israel. How about a small amount of solidarity with them?
Henrik Jordahl on Swedish education and its privatization
Not long ago I linked to an article suggesting there were some burgeoning problems with the Swedish educational privatization model. Henrik wrote me this email:
Dan, Tyler and others!
As the article claims there are really serious problems in Swedish schools – and it does not help that the minister of education from the liberal party does not seem to understand or be willing to admit what is going on.
Importantly, there is no evidence of the private (so called independent) schools or of the introduction of school choice contributing to worse performance. The two most relevant studies establishing this are:
1. Böhlmark, Anders & Lindahl, Mikael, 2013. “Independent Schools and Long-Run Educational Outcomes Evidence from Sweden´s Large Scale Voucher Reform,” Working Paper Series 6/2013, Swedish Institute for Social Research.
http://su.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:675521/FULLTEXT01.pdf Finds that an increase in the share of independent-school students improves average performance at the end of compulsory school as well as long-run educational outcomes. Also finds that international test results (TIMSS) deteriorated less in Swedish regions with a higher proportion of independent school students.2. Wondratschek, Verena, Karin Edmark and Markus Frölich (2013). “The Short- and Long-term Effects of School Choice on Student Outcomes – Evidence from a School Choice Reform in Sweden”, IFN Working Paper No. 981. Forthcoming in Annals of Economics and Statistics. http://www.ifn.se/eng/publications/wp/2013/981 . Finds that increased school choice had very small, but positive, effects on marks at the end of compulsory schooling, but virtually zero effects on longer term outcomes.
Hope this is useful and not too late.
Friedrich A. Hayek class on MRUniversity
MRUniversity.com has a new class on Hayek’s Individualism and Economic Order, free on-line pdf version of the book is here. The class is based around my reread of the book — often considered the single best introduction to Hayek — and what I learned from each chapter., whether positively or negatively.
The MRUniversity videos are now available on the homepage of MRU at the end of the Great Economists section. There is also a landing page for all of the Hayek videos at once.
Overall the book held up very well upon my reread. The most interesting chapters — at least given my initial margins — were Hayek’s liberaltarian take on economic policy and Hayek on the likely evolution of European federalism. Hayek makes the very interesting argument that EU-like institutions will be classical liberal by default, as non-intervention tends to be the focal default point when conflicting nations cannot agree on very much. He thus thinks that supranational institutions, while often motivated by peace at first, over time become an instrument of economic freedom.
We invite you to check out the class, and of course there is more to come.
Kebko on North Carolina’s unemployment insurance experiment
#5: I think Evan is being a bit too broad with his interpretation of the labor market in North Carolina. There have been two distinct phases of labor force adjustments:
1) Between the passage of the law and its implementation, there was a small decrease in unemployment. But, mostly, on net, there was a decrease in employment and a corresponding decrease in labor force participation. The movement was from employment to not-in-labor-force. I don’t know if there is a straightforward way to interpret this, but I don’t believe Evan is addressing it cleanly in the article.
2) After the implementation of the law, labor force participation stabilized. Since that time, there has been a decrease in unemployment and an increase in the Employment to Population ratio. People are moving from unemployment to employment.
The first phase could have a number of interpretations. The second phase is clearly what opponents of Emergency Unemployment Insurance would have predicted. At this point, I think we still need to give it a few months to see if the rebound in the employment to population ratio continues. If it does, then this article by Evan will have been unfortunate.
Here is my post on the issue, with some graphs: http://idiosyncraticwhisk.blogspot.com/2013/12/a-natural-experiment-on-emergency.html
Assorted links
1. Six case studies of writers who changed their minds. On what basis were they picked to contribute? And when you like the writer but not the books.
2. Markets in everything: I want to be Brahms’s German Requiem.
5. The North Carolina experience with cutting unemployment benefits.
6. Leading economists endorse Christmas presents, sort of. And Times Higher Ed best books list, deep and broad.
Shiller on Trills
In this short piece, Robert Shiller explains one of the basic ideas of his work on macro markets:
The governments of the world should issue shares in their GDPs, securities that pay to investors as dividends a specified fraction of GDP, in perpetuity (or until the government buys them back on the open market). Governments need to end their historic reliance on debt financing: governments issuing shares in GDP is analogous to corporations issuing equity. My Canadian colleague Mark Kamstra and I propose issuing trillionth shares in GDP, and so to call these “Trills.” Last year, a U.S. Trill would have paid $15.09 in dividends, a Canadian Trill C$1.72. The dividends will change every year as GDP is announced, and predicting these changes will certainly interest investors, just as in the stock market. Governments can auction off Trills when current government debt comes due and needs to be refinanced, as part of a debt reduction program.
In this piece, Shiller focuses on the benefits of Trills as opposed to debt:
Substituting Trills for conventional debt helps deleverage the government, something whose importance has become very clear with the debt crisis in Europe. The payments required of the government by the Trills is connected to the country’s ability to pay, measured by their GDP.
Trills could also be the foundation for many types of insurance products, for example, products that would pay off when GDP was down helping to alleviate business cycle issues. A market in Trills could also be used to make predictions and to judge policies (see Gurkaynak and Wolfers for an early test). Which policies will most increased the value of future trills? Similarly, by looking at how the market for trills changes as the Iowa Political Markets change we could identify which politicians are best for GDP (not just the equity and bond markets).
I featured Shiller’s work on macro markets in my book Entrepreneurial Economics: Bright Ideas from the Dismal Science. I think of this body of work as his most visionary and deserving of the Nobel.
Economic convergence between black immigrants and black natives
Alison Jane Rauh, a job candidate from the University of Chicago, has a new (job market) paper on this topic. The abstract is full of information:
The number of black immigrants living in the US has increased 13-fold from 1970 to 2010, increasing their share of the black population from 1% to 10%. Black immigrants’ labor market outcomes surpass those of native blacks. This paper determines in how far the relative success of black immigrants is passed on to the second generation. While blacks of the second generation have equal or higher education and earnings levels than the first generation, the return on their unobservable characteristics is converging to that of native blacks. Race premia are put into a broader context by comparing them to Hispanics, Asians, and whites. Blacks are the only group that experiences a decrease in residual earnings when moving from the first to the second generation. Black immigrants do not only converge to native blacks across generations but also within a generation. For Asians and Hispanics, residual earnings decrease monotonically with age of immigration. For blacks, the residual earnings-age of immigration profile is upward sloping for those immigrating before the age of 15. Convergence across generations is mostly driven by low-educated second generation blacks that drop out the labor force in greater numbers than low-educated first generation immigrants do. Similarly, convergence within a generation is mostly driven by low-educated blacks who immigrate when they are young dropping out of the labor force in greater numbers than those who immigrate when they are older. A social interactions model with an assimilation parameter that varies by age of immigration helps explain this phenomenon. When making their labor force participation decision, immigrant men of all races, but not women, generally place more weight on the characteristics of natives the earlier they immigrate.
I take this to be a “peer effects are really really important” paper, namely that many of the virtues of immigrant culture are swallowed as the second generation assimilates. I should note that the contents of this paper are interesting throughout, for instance: “Conditional and unconditional annual earnings of native black women are at 91% and 78% of white women, which points to a much more equal distribution than that of men (64% and 78%).”
Here is the abstract of another paper (pdf) by Alison, entitled “Successful Black Immigrants Narrow Black-White Achievement Gaps”:
The number of black immigrants in the US quadrupled from 1980 to 2010, increasing their share of the black population from 4% to 10%. During that time period the black-white wage and employment gap widened substantially. This paper explores the extent native blacks differ from immigrant blacks. Additionally it determines in how far increased selective immigration masks an even greater deterioration in the economic condition of native blacks. In 2011, excluding black immigrants increases the white-black wage gap by 4% for men and 9% for women. It increases the employment gap by 13% and 19% for men and women respectively.
Here is the author’s home page. I hope she gets a very good job.
Who disapproves of Obamacare?
I was somewhat surprised by these numbers:
Fifty-three percent of the uninsured disapprove of the law, the poll found, compared with 51 percent of those who have health coverage. A third of the uninsured say the law will help them personally, but about the same number think it will hurt them, with cost a leading concern.
I wonder if any of this poll was conducted in Spanish, and if not whether that would have changed the results. I found this interesting too:
Of the uninsured who said they were not likely to sign up by the deadline, fully half said it was because of the high cost. Twenty-nine percent said they planned to go without coverage because they object to the government’s requiring it, and 11 percent said they did not need health insurance.
And this:
Seventy-seven percent of the uninsured said they disapproved of the mandate, compared with 65 percent of those who already have health insurance.
Chinese translation of *Modern Principles*
There is now a Chinese translation out of Modern Principles, our Principles text.
Information (in Chinese) on the macro text is here. Information about the micro text is here. You will note that China is a key example in our discussion of catch-up Solow growth, a topic neglected by many other leading Principles textbooks.
For basic information on the English language version of the book, see here.
Assorted links
2. The dangers of barter with gingerbread biscuit tickets. And Izabella Kaminska on shadow banking as free banking.
3. Clemens reviews Collier on immigration.
4. Will drones revolutionize agriculture?
6. Pre-order the new Murakami book here, due out in August.
7. More excellent John Cochrane on the Nobel Laureates and finance. And behavioral economics at the movies.
What predicts the differential impact of the taper?
There is a new paper by Eichengreen and Gupta (pdf):
In May 2013, Federal Reserve officials first began to talk of the possibility of tapering their security purchases. This tapering talk had a sharp negative impact on emerging markets. Different countries, however, were affected very differently. We use data for exchange rates, foreign reserves and equity prices between April and August 2013 to analyze who was hit and why. We find that emerging markets that allowed the real exchange rate to appreciate and the current account deficit to widen during the prior period of quantitative easing saw the sharpest impact. Better fundamentals (the budget deficit, the public debt, the level of reserves, the rate of economic growth) did not provide insulation. A more important determinant of the differential impact was the size of the country’s financial market: countries with larger markets experienced more pressure on the exchange rate, foreign reserves and equity prices. We interpret this as investors being able to better rebalance their portfolios when the target country has a relatively large and liquid financial market.
You can think of this as a step in building a new theory of the non-neutrality of money. The suggestion it seems is that liquidity begets further liquidity, a’ la Matthew. Here is a related and non-gated FT post about “the fragile five.”