Month: August 2014
Political booms, financial crises
There is a new paper by Helios Herrera, Guillermo Ordoñez, and Christoph Trebesch and it has a striking result:
We show that political booms, measured by the rise in governments’ popularity, predict financial crises above and beyond other better-known early warning indicators, such as credit booms. This predictive power, however, only holds in emerging economies. We show that governments in emerging economies are more concerned about their reputation and tend to ride the short-term popularity benefits of weak credit booms rather than implementing politically costly corrective policies that would help prevent potential crises. We provide evidence of the relevance of this reputation mechanism.
Matt Yglesias on Tyler Cowen
Which is to say that while Cowen’s point about the global picture is both interesting and correct, his political stance is backwards. It’s not fans of Capital in the 21st Century who are pushing nationalism as an alternative to plutocracy, but its detractors. And though the recent politics in the US Congress have been driven by the somewhat odd sequence of events around the arrival of unaccompanied minors from Central America, the underlying pattern runs much deeper than that.
I don’t have an “he says exactly that” quotation to pull from Matt’s piece, but I believe he is saying I (or someone?) should be a Progressive instead of a “conservative economist” as he calls me. The article is interesting throughout.
My framing of course is different. It is not about who are the best people, but rather which are the best set of positions. Just to summarize, I generally favor much more immigration but not open borders, I am a liberal on most but not all social issues, and I am market-oriented on economic issues. On most current foreign policy issues I am genuinely agnostic as to what exactly we should do but skeptical that we are doing the right thing at the moment. I don’t like voting for either party or for third parties.
The economics of cyclone disasters
It’s not quite the Solow model. Here is a new paper from Solomon M. Hsiang and Amir S. Jin, “The Causal Effect of Environmental Catastrophe on Long-Run Economic Growth: Evidence From 6,700 Cyclones,” the abstract is this:
Does the environment have a causal effect on economic development? Using meteorological data, we reconstruct every country’s exposure to the universe of tropical cyclones during 1950-2008. We exploit random within-country year-to-year variation in cyclone strikes to identify the causal effect of environmental disasters on long-run growth. We compare each country’s growth rate to itself in the years immediately before and after exposure, accounting for the distribution of cyclones in preceding years. The data reject hypotheses that disasters stimulate growth or that short-run losses disappear following migrations or transfers of wealth. Instead, we find robust evidence that national incomes decline, relative to their pre-disaster trend, and do not recover within twenty years. Both rich and poor countries exhibit this response, with losses magnified in countries with less historical cyclone experience. Income losses arise from a small but persistent suppression of annual growth rates spread across the fifteen years following disaster, generating large and significant cumulative effects: a 90th percentile event reduces per capita incomes by 7.4% two decades later, effectively undoing 3.7 years of average development. The gradual nature of these losses render them inconspicuous to a casual observer, however simulations indicate that they have dramatic influence over the long-run development of countries that are endowed with regular or continuous exposure to disaster. Linking these results to projections of future cyclone activity, we estimate that under conservative discounting assumptions the present discounted cost of “business as usual” climate change is roughly $9.7 trillion larger than previously thought.
That link has an NBER gate, I do not yet see an ungated version.
Assorted links
Is growing income inequality diminishing middlebrow culture?
A.O. Scott considers that question in The New York Times. I am not sure I can sum up his view in a sentence, so I don’t know if this is criticizing him or partially agreeing with him. In any case, I don’t see growing income inequality as the main driving force behind the decline of middlebrow American culture. An individual’s level of education often predicts cultural consumption better than does his or her income, and education has not in general declined in this country.
Furthermore many forms of culture have grown much cheaper. Once you are paying for cable, the marginal dollar cost of watching a show or a movie at home is zero. Songs and music are much cheaper than twenty years ago, and eBooks make many (not all) books cheaper. In other words, if stagnant income groups wanted middlebrow culture, they still could afford it.
Global markets are growing and those markets are often relatively middlebrow in their orientation, which should maintain the return to producing middlebrow culture. And the United States continues to grow in population, even though the middle is shrinking in percentage terms. The supply of creative activity is quite elastic, so it is hard to argue the wealthy have placed all relevant artists in their employ and thus choked or starved the middle.
It is much more expensive to organize a middlebrow art exhibit than fifteen years ago, and we see fewer good ones, but that is mainly because of 9/11 and insurance rates and related institutional issues, not income inequality.
My view is a lot of people never wanted middlebrow culture in the first place, at least not in every sphere of their cultural consumption. The internet gave them more choice, they took it, and much of middlebrow culture lost its support base. Consider one area where the internet still doesn’t play that much of a role and that is theatrical productions. You can watch plenty of theatre on YouTube, but it’s not such a close substitute to seeing the show live. And if you look at Broadway theatre, it seems more relentlessly and aggressively middlebrow than ever before. Ugh, that is why I stopped going. NFL football seems middlebrow to me and the audience base still is there, again because the internet has not come up with a close competitor. If the sport has a problem it is the violence and injury, not that we’ve evolved into a mix of polo ponies and roller derby.
The separate door
In an age of widening inequality, in a city with ever-more expensive rent, the “poor door” has become an outsized symbol.
Technically, it doesn’t exist yet. But earlier this month, New York City approved plans for a high-rise apartment in Manhattan that will include it: a separate entrance for the property’s subsidized tenants. The luxury condo will otherwise have more than 150 market-rate apartments. But its 55 affordable units, offered by the developer Extell through the city’s inclusionary housing program, will be separated with different amenities, different views of the city and, yes, a different front door.
A housing complex in DC soon may be trying the same.
Sentences about poverty
The number of distressed neighborhoods in the suburbs grew by nearly 140 percent, compared to 50 percent in urban areas.
That is since 2000, from Danielle Kurtzleben.
Assorted links
1. NFL players height and weight over time.
2. Why are start-ups slowing down?
3. Some material goods can make you happy.
4. On the Saudi-Israel “alliance.”
5. Mankiw on a reader on Sowell on sincerity, a very good point.
6. Lawyers without law school.
7. Really bad food markets in everything, potato chip edition.
Monopsony and its drawbacks
The Bully Fire, which has burned more than 12,600 acres in Shasta County, is nearly contained. In the two weeks since it ignited, about 2,000 firefighters have battled the blaze. Nearly half of them — 900 — are inmates with the California Department of Corrections. These “low-level offenders” making just $2 a day are a crucial component in how the state battles wildfires.
Yet there is some extra compensation:
Once they’re in the program they never spend a night in a prison facility.
Nonetheless:
A few other men say they might try firefighting when they’re released, but most, citing the hot, hard work and long hours, say, “No way.”
There is more here, via Michael Makowsky.
Ghana isn’t doing as well as many people think
Ghana will turn to the International Monetary Fund for help after the west African country’s currency plunged roughly 40 per cent this year against the dollar, making the cedi the worst performing currency in the world in 2014.
Nearly three years after the start of oil production, which was meant to further strengthen the country’s fiscal position, the public purse is looking empty. Ghana is battling a double-digit fiscal deficit after a 75 per cent increase in public salaries over two years. Inflation is rising rapidly as the cedi plunges.
Ghana ran a fiscal deficit equal to 10.1 per cent of gross domestic product in 2013. The government has promised to lower the deficit to 8.5 per cent this year, but observers believe it would struggled to reduce it below 10 per cent.
The full FT story is here, here are ungated sources, here is one account from Ghana.
Assorted links
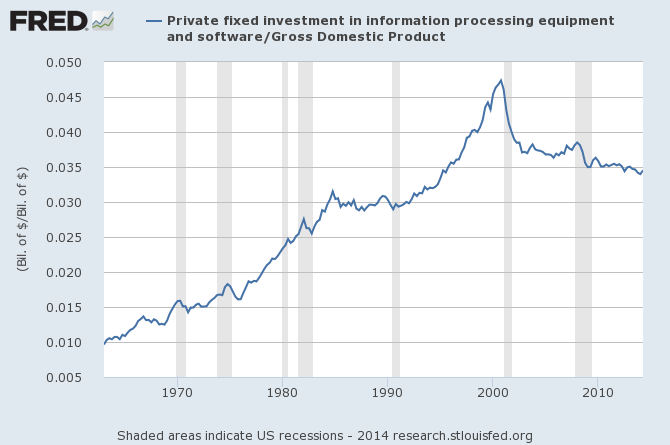
U.S. IT investment as a share of gdp
The pointer is from Matt Yglesias.
Addendum: Claudia Sahm refers us to this chart of declining IT prices. It also can be argued that IT spending moved into other, more general business categories.
What I’ve been reading
1. Walter Lippmann: Public Economist, by Craufurd D. Goodwin. An excellent study of the man who was probably the most influential economics columnist and commentator of his era, even though he is not usually remembered as such.
2. The Alliance: Managing Talent in the Networked Age, by Reid Hoffman, Ben Casnocha, and Chris Yeh. A popular book on how a lot of future jobs will be very short-term and how to deal with this world on a practical basis.
3. Jonathan Rottenberg, The Depths: The Evolutionary Origins of the Depression Epidemic. More intelligent and thoughtful than most other books in this area, this treatment stresses the (partial) cognitive advantages of having a tendency toward depression.
4. David Eimer, The Emperor Far Away: Travels at the Edge of China. A look at China’s outermost regions and their ethnic minorities, an excellent perspective on The Middle Kingdom.
5. Steven Conn, Americans Against the City: Anti-Urbanism in the Twentieth Century. Good background for understanding today’s blue-red divide and the origins of progressivism.
6. Lawrence A. Cunningham, Berkshire Beyond Buffet: The Enduring Value of Values. Maybe the title doesn’t sound promising, but this is a substantive take on what actually goes on out there.
Arrived in my pile are:
6. Paul Know, editor, Atlas of Cities.
7. Dan DiSalvo, Government Against Itself: Public Union Power and Its Consequences.
8. Stephen L. Carter, Back Channel: A Novel.
Russia fact of the day
Shares in Gazprom, a company that made $32bn in net income last year, trade at only 2.6 times forward earnings.
That is from FTAlphaville.