Category: Current Affairs
Claims about China
Tariffs don’t just alter trade flows — they redirect resources and reshape industrial structures. If Trump’s goal was to curb China’s technological progress, he would keep tariffs low on the bulk of Chinese exports to the US, locking the country into low-margin basic manufacturing. He would encourage high-tech exports to China, making sure that progress in its advanced components stalls.
But this is the opposite of what’s happening. Ironically, just as the “China shock” pushed the US out of low-end manufacturing, the “Trump shock” is propelling China to reallocate resources into higher value, advanced technologies that compete directly with the US.
Here is more from Keyu Jin at the FT.
My Conversation with the excellent Jennifer Pahlka
Here is the audio, video, and transcript. Here is the episode summary:
Jennifer Pahlka believes America’s bureaucratic dysfunction is deeply rooted in outdated processes and misaligned incentives. As the founder of Code for America and co-founder of the United States Digital Service, she has witnessed firsthand how government struggles to adapt to the digital age, often trapped in rigid procedures and disconnected from the real-world impact of its policies. Disruption is clearly needed, she says—but can it be done in a way that avoids the chaos of DOGE?
Tyler and Jennifer discuss all this and more, including why Congress has become increasingly passive, how she’d go about reforming government programs, whether there should be less accountability in government, how AGI will change things, whether the US should have public-sector unions, what Singapore’s effectiveness reveals about the trade-offs of technocratic governance, how AI might fundamentally transform national sovereignty, what her experience in the gaming industry taught her about reimagining systems, which American states are the best-governed, the best fictional depictions of bureaucracy, how she’d improve New York City’s governance, her current work at the Niskanen Center, and more.
Excerpt:
COWEN: Does that mean we need something like DOGE? I’ve lived near DC for about 40 years of my life. I haven’t seen anyone succeed with regulatory reforms. You can abolish an agency, but to really reform the process hasn’t worked. Maybe the best iteration we can get is to break a bunch of things now. That will be painful, people will hate it, but you have a chance in the next administration to put some of them back together again.
Maybe it’s just in a large country, there’s no other way to do it. We have separation of powers. The first two years of DOGE will seem terrible, but 8, 12, 16 years from now, we’ll be glad we did it. Is that possible?
PAHLKA: I don’t know what’s going to happen. I do think this is the disruption that we’re getting, whether it’s the disruption we wanted. The question of whether it could have been done in a more orderly manner is a tough one. I just feel sad that we didn’t try.
COWEN: Are you sure we didn’t try?
PAHLKA: I don’t think we really tried.
COWEN: The second Bush presidency, people talked about this, what we need to do. Al Gore — some of that was good, in fact, reinventing government. We’ve been trying all along, but this is what trying looks like.
PAHLKA: Yes. I think reinventing government happened at a time when we were just at the beginning of this digital revolution. It was trying with a very 20th-century mindset. Fine, did well within that context, but we don’t need that again.
We need 21st century change. We need true digital transformation. We need something that’s not stuck in the industrial ways of thinking. I don’t think we tried that. I think the efforts have just been too respectful of old ways of working and the institutions. There was really not an appetite, I think, for what I would call responsible disruptive change. Would it have worked?
COWEN: Is there such a thing?
PAHLKA: I don’t know. [laughs]
COWEN: Say you’re approaching USAID, where I think the best programs are great. A lot of it they shouldn’t be doing. On net, it passes a cost-benefit test, but the agency internally never seemed willing to actually get rid of the bad stuff, all the contracting arrangements which made American Congress people happy because it was dollars sent to America, but way inflated overhead and fixed costs. Why isn’t it better just to blow that up — some of it is great — and then rebuild the great parts?
PAHLKA: It’s so hard to say. [laughs] I’ve had the same thought. In fact, before inauguration, I wrote about the Department of Defense. It’s the same thing. There’s a clear recognition by the people in the institution, as you saw with USAID, that this is not okay, that this is not working. It’s just strange to be in an institution that large where so many people agree that it’s not working, from the bottom to the top, and yet nobody can make really substantive change.
Of great interest, obviously.
AI on Tariffs
There is some evidence that the White House used AI to come up with a quick and dirty (and incorrect) formula to correlate tariff rates with trade deficits. I have no problem with using AI, I think they just didn’t go far enough. The White House should have asked the AI a question like this:
Suppose the US imposed tariffs on other countries in an effort to reduce bilateral trade deficits to zero using the formula for the tariff of (exports-imports)/imports. What do you estimate would be the consequences of such a policy?
Answer (O1 Pro):
A tariff schedule keyed to bilateral deficits—imposing a rate equal to (US exports − US imports) / US imports—would be extremely disruptive and unlikely to achieve its goal. Key points:
Immediate Impact on Prices and Supply Chains
If the US imports more than it exports from a given country, (exports − imports) is negative, making the tariff percentage negative unless the formula is modified (e.g., by absolute value). In practice, one would presumably set a positive tariff aimed at closing the bilateral gap.
Such high tariffs would sharply raise import prices for both consumers and firms reliant on foreign inputs. It would encourage attempts to switch suppliers but at the cost of disrupting supply chains and increasing production expenses.
Retaliation and Trade War Dynamics
Targeted countries would almost certainly retaliate with their own tariffs. Retaliation would damage US export sectors—especially agriculture and high-value manufacturing—and risk a broader trade war.
Countries with a US trade surplus would apply punitive measures that shift US business to alternative suppliers, undermining the very exports the policy is meant to foster.
Misalignment with Macroeconomic Fundamentals
Bilateral imbalances reflect global production patterns, comparative advantage, and macro factors like savings–investment imbalances and currency flows. A country that persistently imports more overall does so because it’s running a capital account surplus. Tariffs don’t fundamentally alter that global saving–investment arithmetic.
If the US still runs an overall current account deficit, restricting imports from some countries will simply shift deficits to others. Global supply chains will rearrange, but the total US deficit will be largely unchanged.
Violation of Trade Agreements
Such a policy almost certainly violates WTO rules, since it imposes discriminatory tariffs based on bilateral imbalances. The resulting litigation and sanctions would add more uncertainty.
Net Effect: Reduced Efficiency, Higher Costs
Economically, the net effect is negative. Costs rise for US consumers and US manufacturers reliant on imported inputs. Retaliatory measures reduce export opportunities. Overall trade volume shrinks. Growth slows, and no fundamental improvement in the US external balance occurs.
In summary, a bilateral “deficit-equalizing” tariff policy would create severe distortions, invite retaliation, and do little to fix the structural causes of US trade deficits. Empirical evidence and standard trade theory both suggest it would reduce economic efficiency and likely harm US producers and consumers alike.
Good answer.
Hat tip: SB.
A Blueprint for FDA Reform
The new FDA report from Joe Lonsdale and team is impressive. It has a lot of new material, is rich in specifics and bold in vision. Here are just a few of the recommendation which caught my eye:
From the prosaic: GMP is not necessary if you are not manufacturing:
In the U.S., anyone running a clinical trial must manufacture their product under full Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regardless of stage. This adds enormous cost (often $10M+) and more importantly, as much as a year’s delay to early-stage research. Beyond the cost and time, these requirements are outright irrational: for example, the FDA often requires three months of stability testing for a drug patients will receive after two weeks. Why do we care if it’s stable after we’ve already administered it? Or take AAV manufacturing—the FDA requires both a potency assay and an infectivity assay, even though potency necessarily reflects infectivity.
This change would not be unprecedented either. By contrast, countries like Australia and China permit Phase 1 trials with non-GMP drug with no evidence of increased patient harm.
The FDA carved out a limited exemption to this requirement in 2008, but its hands are tied by statute from taking further steps. Congress must act to fully exempt Phase 1 trials from statutory GMP. GMP has its place in commercial-scale production. But patients with six months to live shouldn’t be denied access to a potentially lifesaving therapy because it wasn’t made in a facility that meets commercial packaging standards.
Design data flows for AIs:
With modern AI and digital infrastructure, trials should be designed for machine-readable outputs that flow directly to FDA systems, allowing regulators to review data as it accumulates without breaking blinding. No more waiting nine months for report writing or twelve months for post-trial review. The FDA should create standard data formats (akin to GAAP in finance) and waive documentation requirements for data it already ingests. In parallel, the agency should partner with a top AI company to train an LLM on historical submissions, triaging reviewer workload so human attention is focused only where the model flags concern. The goal is simple: get to “yes” or “no” within weeks, not years.
Publish all results:
Clinical trials for drugs that are negative are frequently left unpublished. This is a problem because it slows progress and wastes resources. When negative results aren’t published, companies duplicate failed efforts, investors misallocate capital, and scientists miss opportunities to refine hypotheses. Publishing all trial outcomes — positive or negative—creates a shared base of knowledge that makes drug development faster, cheaper, and more rational. Silence benefits no one except underperforming sponsors; transparency accelerates innovation.
The FDA already has the authority to do so under section 801 of the FDAAA, but failed to adopt a more expansive rule in the past when it created clinicaltrials.gov. Every trial on clincaltrials.gov should have a publication associated with it that is accessible to the public, to benefit from the sacrifices inherent in a patient participating in a clinical trial.
To the visionary:
We need multiple competing approval frameworks within HHS and/or FDA. Agencies like the VA, Medicare, Medicaid, or the Indian Health Service should be empowered to greenlight therapies for their unique populations. Just as the DoD uses elite Special Operations teams to pioneer new capabilities, HHS should create high-agency “SWAT teams” that experiment with novel approval models, monitor outcomes in real time using consumer tech like wearables and remote diagnostics, and publish findings transparently. Let the best frameworks rise through internal competition—not by decree, but by results.
…Clinical trials like the RECOVERY trial and manufacturing efforts like Operation Warp Speed were what actually moved the needle during COVID. That’s what must be institutionalized. Similarly, we need to pay manufacturers to compete in rapidly scaling new facilities for drugs already in shortage today. This capacity can then be flexibly retooled during a crisis.
Right now, there’s zero incentive to rapidly build new drug or device manufacturing plants because FDA reviews move far too slowly. Yet, when crisis strikes, America must pivot instantly—scaling production to hundreds of millions of doses or thousands of devices within weeks, not months or years. To build this capability at home, the Administration and FDA should launch competitive programs that reward manufacturers for rapidly scaling flexible factories—similar to the competitive, market-driven strategies pioneered in defense by the DIU. Speed, flexibility, and scale should be the benchmarks for success, not bureaucratic checklists. While the drugs selected for these competitive efforts shouldn’t be hypothetical—focus on medicines facing shortages right now. This ensures every dollar invested delivers immediate value, eliminating waste and strengthening our readiness for future crises.
To prepare for the next emergency, we need to practice now. That means running fast, focused clinical trials on today’s pressing questions—like the use of GLP-1s in non-obese patients—not just to generate insight, but to build the infrastructure and muscle memory for speed.
Read the whole thing.
Hat tip: Carl Close.
A contagion of uncertainty
That is my latest piece for The Free Press, here is one excerpt:
It is not merely that the policies keep on changing. We are seeing that the policies didn’t have much of a rational basis to begin with. Exactly how were all those threatened tariff rates calculated to begin with? A debate is raging across the internet and social media, but it seems they did not have much of a logical basis. We even were ready to put a tariff rate of 10 percent on the Heard Island and McDonald Islands (where?), which are inhabited mostly by penguins.
Not a single step of this process has inspired confidence. A variety of people are trying to defend the Trump plans on social media, but with markets plummeting they have not been convincing. We saw a three-day market loss of about 13 percent, and no coherent government response.
Who in the Trump administration has presented any account of its policies to the public with any degree of knowledge, competence, or credible reassurance? What I have seen is Secretary of Commerce Howard Lutnick speaking about the new jobs Americans might have assembling iPhones, something which currently would most likely be done in a Chinese factory. Who is supposed to be thrilled by that vision of the American future? Or should we be reassured by the possibility that Lutnick did not mean that remark literally, but instead was speaking out of mere carelessness?
One lesson I am learning — yet again — is just how many people will defend a status quo backed by power…
Manufacturing and Trade
It has become popular in some circles to argue that trade—or, in the more “sophisticated” version, that the dollar’s reserve-currency status—undermines U.S. manufacturing. In reality, there is little support for this claim.
Let’s begin with some simple but often overlooked points.
- The US is a manufacturing powerhouse. We produce $2.5 trillion of value-added in manufacturing output, more than ever before in history.
- As a share of total employment, employment in manufacturing is on a long-term, slow, secular trend down. This is true not just in the United States but in most of the world and is primarily a reflection of automation allowing us to produce more with less. Even China has topped out on manufacturing employment.
- A substantial majority of US imports are for intermediate goods like capital goods, industrial supplies and raw materials that are used to produce other goods including manufacturing exports! Tariffs, therefore, often make it more costly to manufacture domestically.
- The US is a big country and we consume a lot of our own manufacturing output. We do export and import substantial amounts, but trade is not first order when it comes to manufacturing. Regardless of your tariff theories, to increase manufacturing output we need to increase US manufacturing productivity by improving infrastructure, reducing the cost of energy, improving education, reducing regulation and speeding permitting. You can’t build in America if you can’t build power plants, roads and seaports.
- The US is the highest income large country in the world. It’s hard to see how we have been ripped off by trade. China is much poorer than the United States.
- China produces more manufacturing output than the United States, most of which it consumes domestically. China has more than 4 times the population of the United States. Of course, they produce more! India will produce more than the United States in the future as well. Get used to it. You know what they say about people with big shoes? They have big feet. Countries with big populations. They produce a lot. More Americans would solve this “problem.”
- Most economists agree that there are some special cases for subsidizing and protecting a domestic industry, e.g. military production, vaccines.
The seven points cover most of the ground but more recently there has been an argument that the US dollar’s status as a reserve currency, which we used to call the “exorbitant privilege,” is now somehow a nefarious burden. This strikes me as largely an ex-post rationalization for misguided policies, but let’s examine the core claim: the US’s status as a reserve currency forces the US dollar to appreciate which makes our exports less competitive on world markets. Tariffs are supposed to (somehow?) depreciate the currency solving this problem. Every step is questionable. Note, for example, that tariffs tend to appreciate the dollar since the supply of dollars declines. Note also that if even if tariffs depreciated the currency, depreciating the currency doesn’t help to increase exports if you have cut imports (see Three Simple Principles of Trade Policy). I want to focus, however, on the first point does the US status as world reserve currency appreciate the dollar and hurt exports? This is mostly standard economics so its not entirely wrong but I think it misses key points even for most economists.
Countries hold dollars to facilitate world trade, and this benefits the United States. By “selling” dollars—which we can produce at minimal cost (albeit it does help that we spend on the military to keep the sea lanes open)—we acquire real goods and services in exchange, realizing an “exorbitant privilege.” Does that privilege impose a hidden cost on our manufacturing sector? Not really.
In the short run, increased global demand for dollars can push up the exchange rate, making exports more expensive. Yet this effect arises whatever the cause of the increased demand for dollars. If foreigners want to buy more US tractors this appreciates the dollar and makes it more expensive for foreigners to buy US computers. Is our tractor industry a nefarious burden on our computer industry? I don’t think so but more importantly, this is a short-run effect. Exchange rates adjust first, but other prices follow, with purchasing power parity (PPP) tendencies limiting any long-term overvaluation.
To see why, imagine a global single-currency world (e.g., a gold standard or a stablecoin pegged to the US dollar). In this scenario, increased demand for US assets would primarily lead to lower US interest rates or higher US asset prices, equilibrating the market without altering the relative price of US goods through the exchange rate mechanism. With freely floating exchange rates, the exchange rate moves first and the effect of the increased demand is moderated and spread widely but as other prices adjust the long-run equilibrium is the same as in a world with one currency. There’s no permanent “extra” appreciation that would systematically erode manufacturing competitiveness. Notice also that the moderating effect of floating exchange rates works in both directions so when there is deprecation the initial effect is spread more widely giving industries time to adjust as we move to the final equilibrium.
None of this to deny that some industries may feel short-run pressure from currency swings but these pressures are not different from all of the ordinary ups and down of market demand and supply, some of which, as I hove noted, floating exchange rates tend to moderate.
Ensuring a robust manufacturing sector depends on sound domestic policies, innovation, and workforce development, rather than trying to devalue the currency or curtail trade. Far from being a nefarious cost, the U.S. role as issuer of the world’s reserve currency confers significant financial and economic advantages that, in the long run, do not meaningfully erode the nation’s manufacturing base.
My 2022 piece on the New Right vs. classical liberalism
Worth a redux, here is one excerpt:
While I try my best to understand the New Right, I am far from being persuaded. One worry I have is about how it initially negative emphasis feeds upon itself. Successful societies are based on trust, including trust in leaders, and the New Right doesn’t offer resources for forming that trust or any kind of comparable substitute. As a nation-building project it seems like a dead end. If anything, it may hasten the Brazilianification of the United States rather than avoiding it, Brazil being a paradigmatic example of a low trust society and government.
I also do not see how the New Right stance avoids the risks from an extremely corrupt and self-seeking power elite. Let’s say the New Right description of the rottenness of elites were true – would we really solve that problem by electing more New Right-oriented individuals to government? Under a New Right worldview, there is all the more reason to be cynical about New Right leaders, no matter which ideological side they start on. If elites are so corrupt right now, the force corrupting elites are likely to be truly fundamental…
The New Right also seems bad at coalition building, most of all because it is so polarizing about the elites on the other side. Many of the most beneficial changes in American history have come about through broad coalitions, not just from one political side or the other. Libertarians such as William Lloyd Garrison played a key role an anti-slavery debates, but they would not have gotten very far without support from the more statist Republicans, including Abraham Lincoln. If you so demonize the elites that do not belong to your side, it is more likely we will end up in situations where all elites have to preside over a morally unacceptable status quo…
Perhaps most of all, it is dangerous when “how much can we trust elites?” becomes a major dividing line in society. We’ve already seen the unfairness and cascading negativism of cancel culture. To apply cancel culture to our own elites, as in essence the New Right is proposing to do, is not likely to lead to higher trust and better reputations for those in power, even for those who deserve decent reputations.
Recommended, do read or reread the whole thing.
Why Do Domestic Prices Rise With Tarriffs?
Many people think they understand why domestic prices rise with tariffs–domestic producers take advantage of reduced competition to jack up prices and increase their profits. The explanation seems cynical and sophisticated and its not entirely wrong but it misses deeper truths. Moreover, this “explanation” makes people think that an appropriate response to domestic firms raising prices is price controls and threats, which would make things worse. In fact, tariffs will increase domestic prices even in perfectly competitive industries. Let’s see why.
Suppose we tax imports of French and Italian wine. As a result, demand for California wine rises, and producers in Napa and Sonoma expand production to meet it. Here’s the key point: Expanding production without increasing costs is difficult, especially so for any big expansion in normal times.
To produce more, wine producers in Napa and Sonoma need more land. But the most productive, cost-effective land is already in use. Expansion forces producers onto less suitable land—land that’s either less productive for wine or more valuable for other purposes. Wine production competes with the production of olive oil, dairy and artisanal cheeses, heirloom vegetables, livestock, housing, tourism, and even geothermal energy (in Sonoma). Thus, as wine production expands, costs increases because opportunity costs increase. As wine production expands the price we pay is less production of other goods and services.
Thus, the fundamental reason domestic prices rise with tariffs is that expanding production must displace other high-value uses. The higher money cost reflects the opportunity cost—the value of the goods society forgoes, like olive oil and cheese, to produce more wine.
And the fundamental reason why trade is beneficial is that foreign producers are willing to send us wine in exchange for fewer resources than we would need to produce the wine ourselves. Put differently, we have two options: produce more wine domestically by diverting resources from olive oil and cheese, or produce more olive oil and cheese and trade some of it for foreign wine. The latter makes us wealthier when foreign producers have lower costs.
Tariffs reverse this logic. By pushing wine production back home, they force us to use more costly resources—to sacrifice more olive oil and cheese than necessary—to get the same wine. The result is a net loss of wealth.
Note that tariffs do not increase domestic production, they shift domestic production from one industry to another.
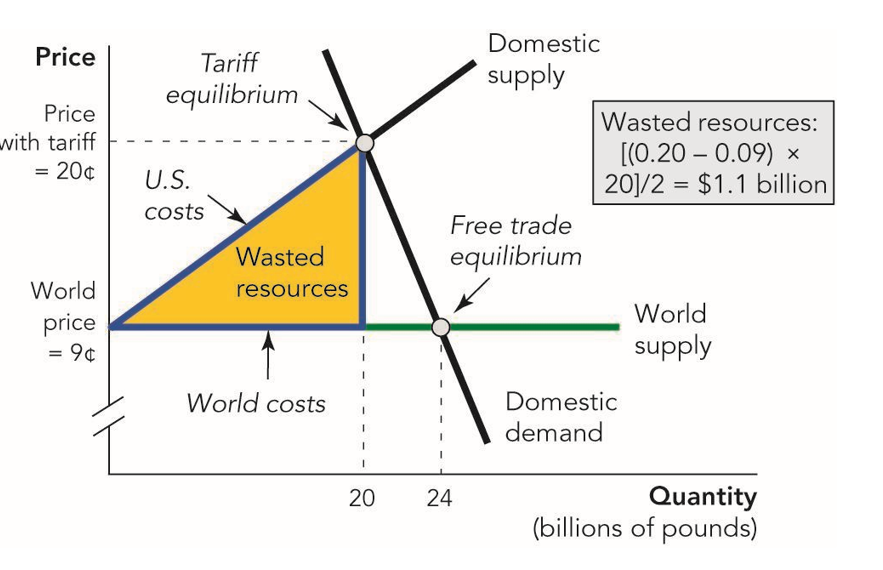
Here’s the diagram, taken from Modern Principles, using sugar as the example. Without the tariff, we could buy sugar at the world price of 9 cents per pound. The tariff pushes domestic production up to 20 billion pounds.
As the domestic sugar industry expands it pulls in resources from other industries. The value of those resources exceeds what we would have paid foreign producers. That excess cost is represented by the yellow area labeled wasted resources—the value of goods and services we gave up by redirecting resources to domestic sugar production instead of using them to produce other goods and services where we have a comparative advantage.
All of this, of course, is explained in Modern Principles, the best textbook for principles of economics. Needed now more than ever.
Russia facts of the day
Russia’s stock market has suffered its worst week in more than two years in response to U.S. President Donald Trump’s sweeping global tariffs and a drop in global oil prices.
The market capitalization of companies listed on the Moscow Exchange (MOEX) fell by 2 trillion rubles ($23.7 billion) over just two days, sliding from 55.04 trillion rubles ($651.8 billion) at Wednesday’s close to 53.02 trillion ($627.9 billion) by the end of trading Friday, according to exchange data.
The MOEX Russia Index, which tracks 43 of Russia’s largest publicly traded companies, lost 8.05% over the week — its worst performance since late September 2022, when markets were rattled by the Kremlin’s announcement of mass mobilization for the war in Ukraine.
At the end of trading on Friday, shares in some of the country’s largest firms had plunged: Sberbank fell by 5.2%, Gazprom 4.9%, VTB 6%, Rosneft 3.9% and Lukoil 4.6%. Mechel, the steel and coal giant, dropped more than 7%, while flagship airline Aeroflot slid 4.8% and gas producer Novatek fell 5.4%.
“A massive crisis is unfolding before our eyes,” said Yevgeny Kogan, an investment banker and professor at the Higher School of Economics in Moscow.
Here is the full story, via C. At least Trump does not seem to be a Russian agent…
Common sense from Ross Douthat
Now for my own view. I think trying to reshore some manufacturing and decouple more from China makes sense from a national security standpoint, even if it costs something to G.D.P. and the stock market. Using revenue from such a limited, China-focused tariff regime to pay down the deficit seems entirely reasonable.
I am more skeptical that such reshoring will alleviate specific male blue-collar social ills, because automation has changed the industries so much that I suspect you would need some sort of social restoration first to make the current millions of male work force dropouts more employable.
And I am extremely skeptical of any plan that treats pre-emptive global disruption as the key to avoiding a deficit crisis down the road. The “instigate a crisis now before our position weakens” has a poor track record in real wars — I don’t think trade wars are necessarily different.
Here is the full NYT piece. And from Armand Domalewski on Twitter: “there is no industry in America with stronger protectionism than the shipbuilding industry. The Jones Act makes it illegal to ship anything between two points in the US on a ship not built in the US and crewed by Americans. And yet America’s shipbuilding industry is nonexistent”
Some modest Congressional rebellion against Trump tariffs?
Let us hope. Via Ben Klutsey.
Yours truly on the Trump tariffs at The Free Press
In any case, we will be moving into a future with higher prices, less product choice, and much weaker foreign alliances. The tanking of the stock market, and other possible asset price repercussions, may tip America into recession and increase joblessness.
This is perhaps the worst economic own goal I have seen in my lifetime. I cannot think of any credentialed economist colleague—Democrat, Republican, or independent—who would endorse it. And I haven’t even mentioned the risk that some foreign nations will retaliate against American exporters, damaging our economy all the more.
You might think there is something to be said for a reciprocal approach to tariffs. Usually it consists of cutting off your nose to spite your face, but if it can sometimes work it requires a president (and Congress) who is predictable and trustworthy.
That is not how foreign nations view the current administration.
If you are wondering about the trade treatment of Canada and Mexico, that remains cloaked in mystery. The threatened 25 percent rate on those two nations, from earlier in Trump’s second term, violates the NAFTA redo that was negotiated by Trump himself. Why trust in reciprocity here?
There is much more at the full link. And yes we are getting government by AI (kudos to Rohit!), but someone didn’t write the proper prompt…
Elon to retreat from DOGE
President Donald Trump has told his inner circle, including members of his Cabinet, that Elon Musk will be stepping back in the coming weeks from his current role as governing partner, ubiquitous cheerleader and Washington hatchet man…
Musk’s looming retreat comes as some Trump administration insiders and many outside allies have become frustrated with his unpredictability and increasingly view the billionaire as a political liability, a dynamic that was thrown into stark relief Tuesday when a conservative judge Musk vocally supported lost his bid for a Wisconsin Supreme Court seat by 10 points.
It also represents a stark shift in the Trump-Musk relationship from a month ago, when White House officials and allies were predicting Musk was “here to stay” and that Trump would find a way to blow past the 130-day time limit.
Here is the full story. I am told frequently that fascism is coming, and recently I was criticized on Twitter (by a German, in German) for discussing DOGE without considering fascism as a kind of essential element of the project. There is plenty to complain about, but this latest development does not sound as if fascism is upon us!? Plus Stefanik is keeping her seat, rather than going to the UN, for electoral reasons, namely wanting to preserve a (slight) GOP majority in the House. So I won’t be moving to Canada, or elsewhere, anytime soon.
The Free Press
This is from the Free Press website, written by me, so I will not indent:
The Free Press is where I have decided to make my new intellectual home.
In a rapidly changing world, I feel The Free Press is the correct base for me, and it has the audience I wish to reach.
First, The Free Press is a start-up.
And because The Free Press is a start-up, it can fail. Many people do not like that fact about start-ups, because they do not want to be part of a possible failure. It means disruption, and also the paycheck stops coming. But I enjoy the risk appetite. It is precisely because it can fail that the people here will work harder, and likely smarter, than the competition.
That it is a start-up is not only true in fact, but you sense it the moment you walk into the newsroom, which I did for the first time recently. The place has overwhelming vibes and energy, and you can feel those in each and every person on the floor.
I think we are entering an era where “floor energy” will matter more than before. It will motivate, define, and lift some institutions well above the others.
A lot of The Free Press is charisma- and personality-based. Much of that comes from Bari Weiss, but there are numerous strong personalities on the roster, covering a wide range of topics, and I know they are keen to bring on even more. I expect the importance of charisma- and personality-based content to rise sharply in the near future.
I don’t know if The Free Press knows this yet, because they tend to be old-school, but pretty soon quality AI programs will write better columns than most of what is considered acceptable at top mainstream media outlets. Of course those columns will not be by human beings, and so those writings will not be able to contextualize themselves within the framework of what a particular individual thinks or feels. That kind of context will be all-important, as impersonal content, based on broadly available public information, will be outcompeted by the machines.
I believe The Free Press intellectual and business model is well-positioned to handle this transition. At The Free Press, and for Free Press readers, the individual writer and personality truly matters, and will continue to matter.
I have written for about 10 years for The New York Times and about eight years for Bloomberg Opinion. Both were wonderful experiences, and I worked with great people and benefited enormously from those relationships. But I am now oh, so very excited about this next step.
Stay tuned for my first official column this Thursday. Click here to make sure you get my work delivered directly to your inbox.
Last but not least: Join Bari and me for a livestream Q+A only for paid members of The Free Press. Come to our website on Thursday, April 3 at 4:30 p.m. ET to watch the conversation.
Sell Floyd Bennett Field!
I’ve been shouting Sell! for many years. Perhaps now is the chance to do it. Here’s a recap:
 The Federal Government owns more than half of Oregon, Utah, Nevada, Idaho and Alaska and it owns nearly half of California, Arizona, New Mexico and Wyoming. See the map (PDF) for more [N.B. the vast majority of this land is NOT parks, AT 2011]. It is time for a sale. Selling even some western land could raise hundreds of billions of dollars – perhaps trillions of dollars – for the Federal government at a time when the funds are badly needed and no one want to raise taxes. At the same time, a sale of western land would improve the efficiency of land allocation.
The Federal Government owns more than half of Oregon, Utah, Nevada, Idaho and Alaska and it owns nearly half of California, Arizona, New Mexico and Wyoming. See the map (PDF) for more [N.B. the vast majority of this land is NOT parks, AT 2011]. It is time for a sale. Selling even some western land could raise hundreds of billions of dollars – perhaps trillions of dollars – for the Federal government at a time when the funds are badly needed and no one want to raise taxes. At the same time, a sale of western land would improve the efficiency of land allocation.
But it’s not just federal lands in the West. Floyd Bennett Field is an old military airport in Brooklyn that hasn’t been used much since the 1970s. Today, it’s literally used as a training ground for sanitation drivers and to occasionally host radio-controlled airplane hobbyists.
In August 2023, state and federal officials reached an agreement to build a large shelter for migrants at Floyd Bennett Field, amid a citywide migrant housing crisis caused by a sharp increase in the number of asylum seekers traveling to the city. The shelter opened that November, but its remote location deterred many migrants. City officials announced plans in December 2024 to close the shelter.

Floyd Bennett Field is over 1000 acres and should be immediately sold to the highest bidder.
Brad Hargreaves on twitter has a good thread with some more examples.
Addendum: Here’s a NPR article (!) from 10 years ago that I am sure still applies even if not in all details:
Government estimates suggest there may be 77,000 empty or underutilized buildings across the country. Taxpayers own them, and even vacant, they’re expensive. The Office of Management and Budget believes these buildings could be costing taxpayers $1.7 billion a year.
…But doing something with these buildings is a complicated job. It turns out that the federal government does not know what it owns.
…even when an agency knows it has a building it would like to sell, bureaucratic hurdles limit it from doing so. No federal agency can sell anything unless it’s uncontaminated, asbestos-free and environmentally safe. Those are expensive fixes.
Then the agency has to make sure another one doesn’t want it. Then state and local governments get a crack at it, then nonprofits — and finally, a 25-year-old law requires the government to see if it could be used as a homeless shelter.
Many agencies just lock the doors and say forget it.