Category: Political Science
Who believes in conspiracy theories?
While the psychological dispositions that underlie conspiracy thinking are well researched, there has been remarkably little research on the political preferences of conspiracy believers that go beyond self-reported ideology or single political issue dimensions. Using data from the European Voter Election Study (EVES), the relationship between conspiracy thinking and attitudes on three deeper-lying and salient political dimensions (redistribution, authoritarianism, migration) is examined. The results show a clear picture: Individuals with economically left-wing and culturally conservative attitudes tend to score highest on conspiracy thinking. People at this ideological location seem to long for both economic and cultural protection and bemoan a “lost paradise” where equalities had not yet been destroyed by “perfidious” processes of cultural modernization and economic neoliberalism. This pattern is found across all countries and holds regardless of socioeconomic characteristics such as education and income. While previous research has found that belief in conspiracies tends to cluster at the extremes of the political spectrum, our analysis opens up a more complex picture, showing that conspiracy thinking is not merely related to extremist orientations, but to specific combinations of political attitudes.
Here is the full article by Florian Buchmayr and André Krouwel, via the excellent Kevin Lewis, who is not obsessed with conspiracy theories.
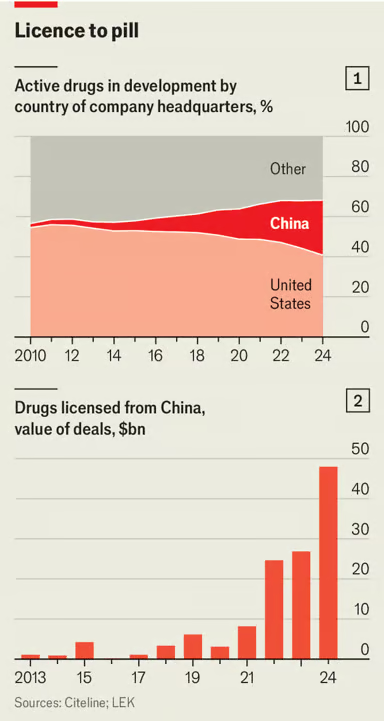
China’s Medicines are Saving American Lives
The Economist reports that China is now the second largest producer of new pharmaceuticals, after the United States.
China has long been known for churning out generic drugs, supplying raw ingredients and managing clinical trials for the pharmaceutical world. But its drugmakers are now also at the cutting edge, producing innovative medicines that are cheaper than the ones they compete with.
… In September last year an experimental drug did what none had done before. In late-stage trials for non-small cell lung cancer, it nearly doubled the time patients lived without the disease getting worse—to 11.1 months, compared with 5.8 months for Keytruda. The results were stunning. So too was the nationality of the biotech company behind them. Akeso is Chinese.
This is exactly what I predicted in my TED talk and it’s great news! As I said then:
Ideas have this amazing property. Thomas Jefferson said “He who receives an idea from me receives instruction himself, without lessening mine. As he who lights his candle at mine receives light without darkening me.”
Now think about the following: if China and India were as rich as the United States is today, the market for cancer drugs would be eight times larger than it is now. Now we are not there yet, but it is happening. As other countries become richer the demand for these pharmaceuticals is going to increase tremendously. And that means an increase incentive to do research and development, which benefits everyone in the world. Larger markets increase the incentive to produce all kinds of ideas, whether it’s software, whether it’s a computer chip, whether it’s a new design.
Well if larger markets increase the incentive to produce new ideas, how do we maximize that incentive?
It’s by having one world market, by globalizing the world. Ideas are meant to be shared.
One idea, one world, one market.
Sadly, some of us are losing sight of the immense benefits of a global market. Another example of the great forgetting.
As Girard predicted, China’s growing similarity to the U.S. has fueled conflict and rivalry. But if managed properly, rivalry can be positive-sum. A rich China benefits us far more than a poor China—including by creating new cancer medicines that save American lives.
Hat tip: Cremieux.
Why Spain’s transition to democracy remains controversial
New podcast series on Latin American political economy, with Rasheed Griffith and Diego Sánchez de la Cruz, all in English.
Caleb Watney on risk and science funding
Right now, DOGE is treating efficiency as a simple cost-cutting exercise. But science isn’t a procurement process; it’s an investment portfolio. If a venture capital firm measured efficiency purely by how little money it spent, rather than by the returns it generated, it wouldn’t last long. We invest in scientific research because we want returns — in knowledge, in lifesaving drugs, in technological capability. Generating those returns sometimes requires spending money on things that don’t fit neatly into a single grant proposal.
While it’s true that indirect costs serve an important function, they can also create perverse incentives: When the government promises to cover expenses, expenses tend to go up. But instead of slashing funding indiscriminately, we should be thinking about how to get the most out of every dollar we invest in science.
That means streamlining research regulations. Universities are drowning in bureaucracy. Since 1990, there have been 270 new rules that complicate how we conduct research. Institutional Review Boards, intended to protect people from being unethically experimented on in studies, now regularly review low-risk social science surveys that pose no real ethical concerns. Researchers generate reams of paperwork in legally mandated disclosures of every foreign contract and collaboration, even for countries such as the Netherlands that present no geopolitical risk.
We must also rethink how we select scientific research to fund.
Caleb is co-CEO of the Institute for Progress, here is more from the NYT.
My excellent Conversation with Ezra Klein
Ezra is getting plenty of coverage for his very good and very on the mark new book with Derek Thompson, Abundance. So far it is a huge hit after only a few days. I figured this conversation would be most interesting, and add the most value, if I tried to push him further from a libertarian point of view (a sign of respect of course). Here is the audio, video, and transcript. Here is part of the episode summary:
In this conversation, Ezra and Tyler discuss how the abundance agenda interacts with political polarization, whether it’s is an elite-driven movement, where Ezra favors NIMBYism, the geographic distribution of US cities, an abundance-driven approach to health care, what to do about fertility decline, how the U.S. federal government might prepare for AGI, whether mass layoffs in government are justified, Ezra’s recommended travel destinations, and more.
Lots of good back and forth, here is one excerpt:
COWEN: Here’s a question from a reader, and I’m paraphrasing. “I can see why you would favor Obamacare and an abundance agenda because Obamacare throws a lot more resources at the healthcare sector in some ways. It did have Medicare cuts, but nonetheless, it’s not choking the sector. But if you favor an abundance agenda, can you then possibly favor single-payer health insurance through the government, which does tend to choke resources and stifle innovation?”
KLEIN: I think it would depend on how you did the single-payer healthcare. Here, we should talk about — because it’s referenced glancingly in the book in a place where you and I differ — but the supervillain view that I hold and your view, which is that you should negotiate drug prices. I’ve always thought on that because I think in some ways, it’s a better toy example than single payer versus Obamacare.
I think you want to take the amount of innovation you’re getting very, very, very seriously. I’ve written pieces about this, that I think if you’re going to do Medicare drug pricing at any kind of significant level, you want to be pairing that with a pretty significant agenda to make drug discovery much easier, to make testing much easier.
And:
COWEN: What should the US federal government do to prepare for AGI? We should just lay off people, right?
KLEIN: [laughs] I would not say it that way. I wouldn’t say just lay off people. I think that’s some of what we’re doing.
COWEN: No, not just, but step one.
KLEIN: Do you think that’s step one? Do you buy this DOGE’s preparation-for-AGI argument that you hear?
COWEN: I think maybe a fifth of them think that. Maybe it’s step two or step three, but it’s a pretty early step, right?
KLEIN: I think that the question of AI or AGI in the federal government, in anywhere — and this is one reason I’ve not bought this argument about DOGE — is you have to ask, “Well what is this AI or AGI doing? What is its value function? What prompt have you given it? What have you asked it to execute across the government and how?”
Alignment, which we have primarily talked about in terms of whether or not the AI, the superintelligence makes us all into paperclips, is a constant question of just near-term systems as well. I think the question of how should we prepare for AGI or for AI in the federal government first has to do with deciding what we would like the AI or the AGI to do. That could be different things to different areas.
My sense — talking to a bunch of people in the companies has helped me conceptualize this better — is that the first thing I would do is begin to ask, what do I think the opportunities of AI are, scientifically and in terms of different kinds of discoveries…
And this:
COWEN: Let me give you another right-wing view, and tell me what you think. The notion that the most important feature of state capacity is whether a state has enough of its citizens willing to fight and die for it. In that case, the United States, Israel, but a pretty small number of nations have high state capacity, and most of Western Europe really does not because they don’t have militaries that mean anything. Is that just the number one feature of abundance in state capacity?
Recommended, obviously.
An Economic Approach to Homer’s Odyssey: Part III
Published by Liberty Fund, by me, here is the third and final installment. Excerpt:
“Below is a brief and simplified catalog of the major polities described in The Odyssey:
- • Pylos and Sparta: Visited by Telemachus, superficially seem normal but they seem sadder on reflection and Sparta relies on intoxication to support public order.
- • Ogygia, or Calypso: An unbearable paradise, there is no utopia.
- • Phaeacia: Relatively well-run, inward-looking, passive-aggressive, “control freak” syndrome.
- • The Lotus Eaters: Another unbearable “utopia.”
- • The Cyclopes: Anarchistic, brutish, and the community is ineffective and unable to defend itself.
- • Aeolus: A closed society, based on incest, hostile to outsiders, a more extreme and dysfunctional version of Phaeacia.
- • Laestrygonia: Giants, they throw boulders and murder, and in some ways resemble the Cyclopes. Tendencies toward anarchy are widespread, and not confined to the Cyclopes.
- • Aeaea (Circe): There is the bed of tyrannical but beautiful Circe, or life as a well-fed pig. Again, utopias are impossible and immortality would bore us.
- • Cimmeria: Dark, bleak, and unloved by God. Possibly the default setting.
- • The Underworld: Everyone is sad (and dead), yet they talk like actual humans and also tell the truth. Lesson: the living cannot escape artifice and deception.
- • Ithaca: Usually wrapped up in war and revenge-taking, chaotic and lacking in trust and lacking in clarity about sovereignty. This is another one of the default options.
- • Syria: Initially prosperous but wrecked by the arrival of avaricious merchants. Unstable.
- • Crete: A diverse society of perfect trust, within a narrative of Odysseus-in-disguise, but it has no chance of existing.”
My overall goal has been to pull out the implicit “public choice” strands in Homer’s Odyssey. It is very much a poem about politics, and the book is among other things a study in comparative politics.
Do read the whole essay, and here are parts one and two.
The political economy of Manus AI
Early reports are pretty consistent, and they indicate that Manus agentic AI is for real, and ahead of its American counterparts. I also hear it is still glitchy Still, it is easy to imagine Chinese agentic AI “getting there” before the American product does. If so, what does that world look like?
The cruder way of putting the question is: “are we going to let Chinese agentic bots crawl all over American computers?”
The next step question is: “do we in fact have a plausible way to stop this from happening?”
Many Chinese use VPNs to get around their own Great Firewall and access OpenAI products. China could toughen its firewall and shut down VPNs, but that is very costly for them. America doesn’t have a Great Firewall at all, and the First Amendment would seem to prevent very tough restrictions on accessing the outside world. Plus there can always be a version of the new models not directly connected to China.
We did (sort of) pass a TikTok ban, but even that applied only to the app. Had the ban gone through, you still could have accessed TikTok through its website. And so, one way or another, Americans will be able to access Manus.
Manus will crawl your computer and do all sorts of useful tasks for you. If not right now, probably within a year or not much more. An American alternative might leapfrog them, but again maybe not.
It is easy to imagine government banning Manus from its computers, just as the state of Virginia banned DeepSeek from its computers. I’m just not sure that matters much. Plenty of people will use it on their private computers, and it could become an integral part of many systems, including systems that interact with the U.S. public sector.
It is not obvious that the CCP will be able to pull strings to manipulate every aspect of Manus operations. I am not worried that you might order a cheeseburger on-line, and end up getting Kung Pao chicken. Still, the data collected by the parent company will in principle be CCP- accessible. Remember that advanced AI can be used to search through that information with relative ease. And over time, though probably not initially, you can imagine a Manus-like entity designed to monitor your computer for information relevant to China and the CCP. Even if it is not easy for a Manus-like entity to manipulate your computer in a “body snatchers-like” way, you can see the points of concern here.
Financial firms might be vulnerable to information capture attacks. Will relatives of U.S. military personnel be forbidden from having agentic Chinese AI on their computers? That does not seem enforceable.
Maybe you’re all worried now!
But should you be?
Whatever problems American computer owners might face, Chinese computer owners will face too. And the most important Chinese computer owner is the CCP and its affiliates, including the military.
More likely, Manus will roam CCP computers too. No, I don’t think that puts “the aliens” in charge, but who exactly is in charge? Is it Butterfly Effect, the company behind Manus, and its few dozen employees? In the short run, yes, more or less. But they too over time are using more and more agentic AIs, perhaps different brands from other companies too.
Think of some new system of checks and balances as being created, much as an economy is itself a spontaneous order. And in this new spontaneous order, a lot of the cognitive capital is coming outside the CCP.
In this new system, is the CCP still the smartest or most powerful entity in China? Or does the spontaneous order of various AI models more or less “rule it”? To what extent do the decisions of the CCP become a derivative product of Manus (and other systems) advice, interpretation, and data gathering?
What exactly is the CCP any more?
Does the importance of Central Committee membership decline radically?
I am not talking doomsday scenarios here. Alignment will ensure that the AI entities (for instance) continue to supply China with clean water, rather than poisoning the water supply. But those AI entities have been trained on information sets that have very different weights than what the CCP implements through its Marxism-swayed, autocracy-swayed decisions. Chinese AI systems look aligned with the CCP, given that they have some crude, ex post censorship and loyalty training. But are the AI systems truly aligned in terms of having the same limited, selective set of information weights that the CCP does? I doubt it. If they did, probably they would not be the leading product.
(There is plenty of discussion of alignment problems with AI. A neglected issue is whether the alignment solution resulting from the competitive process is biased on net toward “universal knowledge” entities, or some other such description, rather than “dogmatic entities.” Probably it is, and probably that is a good thing? …But is it always a good thing?)
Does the CCP see this erosion of its authority and essence coming? If so, will they do anything to try to preempt it? Or maybe a few of them, in Straussian fashion, allow it or even accelerate it?
Let’s say China can indeed “beat” America at AI, but at the cost of giving up control over China, at least as that notion is currently understood. How does that change the world?
Solve for the equilibrium!
Who exactly should be most afraid of Manus and related advances to come?
Who loses the most status in the new, resulting checks and balances equilibrium?
Who gains?
Should OneQuadrillionOwls be worried?
IMO this is one of the more compelling “disaster” scenarios — not that AI goes haywire because it hates humanity, but that it acquires power by being effective and winning trust — and then, that there is a cohort of humans that fear this expansion of trust and control, and those humans find themselves at odds with the nebulously part-human-part-AI governance structure, and chaos ensues.
It’s a messy story that doesn’t place blame at the feet of the AI per se, but in the fickleness of the human notion of legitimacy. It’s not enough to do a good job at governance — you have to meet the (maybe impossible, often contradictory) standards of human citizens, who may dislike you because of what you are or what you represent in some emotional sense.
As soon as any entity (in this case, AI) is given significant power, it has to grapple with questions of legitimacy, and with the thorniest question of all — how shall I deal with people who are trying to undermine my power?
Here is the relevant Reddit thread. Change is tough!
The Ukraine peace deal
The information environment is so soiled right now, it is especially difficult to assess such matters. And I, like many others, am upset about the rhetoric and methods that have been applied from the American side. Nonetheless I think this may be a better deal than its current press indicates. Let me note a few features at the margin, rather than trying to assess the entire situation comprehensively:
1. I don’t know what those mineral rights in Ukraine are worth, but past some level of corruption there is a resource curse (though not for Norway). So losing half of that revenue may not be as bad for Ukraine as it sounds. Was all that oil and gas wealth so good for Russia?
2. For better or worse, the mineral rights deal will, de facto, be renegotiated many times. Read your Williamson and Tirole! So whatever your opinion of what ends up being put on paper this week, think more about solving for the equilibrium over the longer run. The American incentive and willingness to give future aid is now somewhat higher than it would have been, without a mineral rights deal.
3. Since this is Trump’s deal, the Trumpist American right will now have a strong stake in making the deal work. That is significant.
4. At least potentially, Ukraine is now in some funny way “U.S.-certified” by the presence of the mineral rights deal. I do understand the moral hazard problems here, but perhaps the alternative was a slow loss of the war, due to manpower problems of the Ukrainian side.
5. Many people are in denial about how much the current Ukrainian regime, whether justly or not, is unpopular with both Democrats in Congress and with the U.S. deep state. There are far fewer courses of action than many deal critics would like to believe, and it is a mistake to think of all of this as coming from Trump. How exactly would it go trying to push another major Ukraine aid package through Congress?
6. I am not sure what European defense efforts will amount to, but we do see various promises in a constructive direction. Overall I am skeptical, but still there is some motion here.
7. As the prospects for the deal have approached, the Ukraine government bond market has been pretty happy.
So I am hoping for the best, and I consider these views as very subject to rapid revision.
What should I ask Ezra Klein?
Yes I will be doing a podcast with him. And he has a new and very good book coming out with Derek Thompson, namely Abundance. So what should I ask him?
An Economic Approach to Homer’s Odyssey: Part II
My three-part essay for Liberty Fund continues, here is the opener:
In the previous article, I outlined what an economic approach to reading Homer’s epic, The Odyssey,1 might look like. I also noted that what most strikes me about The Odyssey is Homer’s treatment of comparative political regimes. Looking at the wide variety of regimes Odysseus encounters is the focus of this article.
Given that human behavior, at least in The Odyssey, can be understood in terms of the non-standard assumptions described in my previous essay, what are then the possible states of affairs? Which polities might we look to for arranging human interactions and maintaining political order? Utopia is not readily achieved, not only because of material constraints, but also because human behavior is too restless and too desirous of alternative states of affairs. A straightforward order based on political virtue is also beyond human grasp, again because it clashes with the nature of human beings as we understand them. What then might fit with a vision of humans as restless, intoxicating, deceiving, and self-deceiving creatures? The travel explorations of The Odyssey can be understood as, in part, an attempt to address this question.
I will now consider the major and some of the minor polities described by The Odyssey, roughly in the order they appear in the story.
The discussion starts with Pylos and Sparta…
Reforming the NIH
It seems the Trump proposal to simply cut overhead to fifteen percent will not stand up in the courts, at least not without Congressional approval? Nonetheless a few of you have asked me what I think of the idea.
My preferred reforms for the NIH include the following:
1. Cap pre-specified overhead at 25 percent, down from a range running up to 60 percent.
2. Encourage more coverage of overhead in the proposals themselves, where the researchers are accountable for how the overhead funds are spent. Severely limit how much the “overhead” cross-subsidizes other university functions, as is currently the case.
3. Fund a greater number of proposals, with the money coming from overhead reductions, as outlined in #1 and #2.
4. Set up a new, fully independent biomedical research arm of the federal government, based on DARPA-like principles. In fact this was seriously proposed a few years ago, with widespread (but insufficient) support.
I would note a few additional points, which have been covered in earlier MR posts over the years:
5. The NIH could not get its act together during Covid to make fast grants with sufficient rapidity during a time of crisis. They performed much worse than did say the NSF.
6. A while back the NIH set up a program to make riskier grants. The program did not in fact make riskier grants.
7. The NIH killed the idea of an independent DARPA-like biomedical research agency, fearing it would limit the size and influence of the NIH itself.
8. The submission forms, their length, and the associated processes are absurd. Whether or not the costs there are high in an absolute sense, it is a sign the current NIH is far too obsessed with process, as happens to just about every mature bureaucracy.
At this point it is obvious that the NIH cannot reform itself. It is also obvious that a slower, technocratic approach just gives the interest groups — in this case it is “the states” most of all — time to mobilize to protect the current NIH. There are universities in many Congressional districts and a fair amount of money at stake.
I do not per se favor a move to fifteen percent overhead, as I do understand the associated costs on scientific research. Nonetheless I take very seriously the possibility that a radical “thoughtless” cut now stands some chance of getting us to where we ought to be in the longer run, especially since subsequent administrations will get further cracks at this problem. They can up overhead to 25 percent, and set up the new DARPA-H. I just don’t see why that is impossible, and it may not even be unlikely. So what exactly is your discount rate and risk aversion here?
I feel the defenses of the NIH I am reading do not take the entire broader analysis seriously enough. They do not take sufficiently seriously that the writers themselves have failed to adequately reform the NIH. And over time, without serious reform, the bureaucratic stultification will only get worse.
How should government disclosure be done?
That is my recent Bloomberg column on this all-important topic. Here is one part:
The risk is that Trump would hoard the most sensitive information and disclose selectively, to manipulate the news cycle or to distract attention from other events. It also could give him more political weapons to use against what he calls the “deep state.” The president himself is hardly a model of transparency, whether the questions concern his tax returns, his medical exams or the possession of classified documents after leaving office.
But again, the issue is governmental disclosure, and so far, Trump’s record is 0 for 1. Before assuming office, he suggested that the US military knew more than it was letting on about the drones that had been sighted above New Jersey and other Northeastern states. Then, after Trump took office, his press secretary said only that they were “authorized” by the government “for research and various other reasons.” There has been no subsequent attempt to clarify matters. Personally, I am more confused than I was a month ago.
Perhaps there are good national security reasons for this silence. The point is that it is foolish to expect full and open disclosure from the president, no matter what his executive order says or what he has earlier promised.
One way to improve the process would be to appoint some independent auditors on a bipartisan basis, perhaps selected from Congress. Ex post, those auditors could judge whether disclosure, with transparent explanations, had actually occurred. They could grade the degree of disclosure, but they would not have the power to prevent it. Otherwise, there is a risk that — to choose an example not quite at random — evidence favoring the “two gunmen” hypothesis for JFK’s assassination is released, but conflicting evidence for the “lone gunman” hypothesis is suppressed. The auditors would issue a report saying whether disclosure was unbalanced or unfair.
And this:
Another problem with the task force is that it is authorized for only six months. Bureaucracies are by nature slow-moving, and can be even more so when they wish to be. A six-month deadline creates incentives to wait things out. Trump could threaten to extend the mandate, and perhaps he will. But then the disclosure campaign would turn out to be just a bargaining chip, rather than a genuine attempt to bring the truth to light.
Definitely recommended.
What should I ask Jennifer Pahlka?
Yes, I will be doing a Conversation with her. From Wikipedia:
Jennifer Pahlka (born December 27, 1969) is an American businesswoman and political advisor. She is the founder and former executive director of Code for America. She served as U.S. Deputy Chief Technology Officer from June 2013 to June 2014 and helped found the United States Digital Service. Previously she had worked at CMP Media with various roles in the computer game industry. She was the co-chair and general manager of the Web 2.0 conferences. In June 2023, she released the book Recoding America: Why Government Is Failing in the Digital Age and How We Can Do Better.
Recently she has been working on the Niskanen Institute state capacity project. So what should I ask her?
The Effect of European Monarchs on State Performance
We create a novel reign-level data set for European monarchs, covering all major European states between the 10th and 18th centuries. We first document a strong positive relationship between rulers’ cognitive ability and state performance. To address endogeneity issues, we exploit the facts that (i) rulers were appointed according to hereditary succession, independent of their ability, and (ii) the widespread inbreeding among the ruling dynasties of Europe led over centuries to quasirandom variation in ruler ability. We code the degree of blood relationship between the parents of rulers, which also reflects “hidden” layers of inbreeding from previous generations. The coefficient of inbreeding is a strong predictor of ruler ability, and the corresponding instrumental variable results imply that ruler ability had a sizeable effect on the performance of states and their borders. This supports the view that “leaders made history,” shaping the European map until its consolidation into nation states. We also show that rulers mattered only where their power was largely unconstrained. In reigns where parliaments checked the power of monarchs, ruler ability no longer affected their state’s performance.
By Sebastian Ottinger and Nico Voigtländer, from Econometrica. Here are less gated versions. Via the excellent Kevin Lewis.